OVERMOLDING UNDER LOW PRESSURE
Firstly, low-pressure overmolding has won a well-deserved place in the foundry industry. The essence of the method is that the melt under low pressure of air or gas fills the mold.
Excessive pressure in the metal flow is necessary in order to overcome various resistances in its path. The over-molding mold according to this method is filled from the bottom up directly.
Advantages of the low-pressure overmolding method:
- Possibility to automate and mechanize the mold filling process.
- Overmolding quality improves due to excess pressure in the liquid plastic. This makes it possible to obtain over moldings with very thin walls (3-4 mm) and a dense structure.
- The filling of the mold carries out with minimal heat loss on the path of the melt from the furnace to the mold
- The process of automatic filling of the mold cavity with plastic lasts from 1.5 to 6-8 seconds. It depends on the weight of the overmolding. This contributes to an increase in labor productivity.
- The output is overmolding with high mechanical properties, smooth surfaces, and precise geometric shapes. There is no need to machine them.
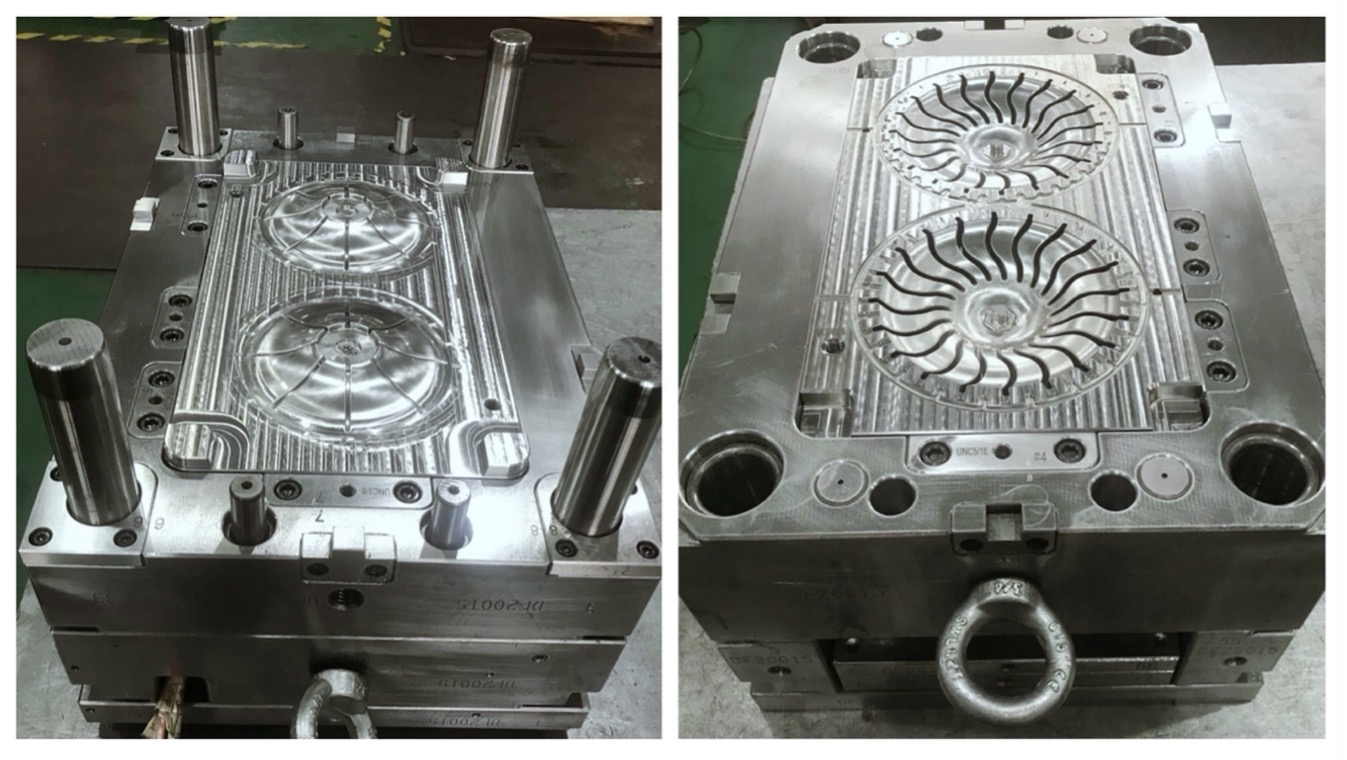
Design and features of the overmolding
The overmolding has a retarding filter, which ensures smooth braking of the rising plastic flow, increasing the static pressure in it, and also avoiding deformation of the sand core. The filter freely passes the air displaced by the alloy from the mold cavity and does not pass the metal. The retarding filter is always made of all metal.
The braking element is a slots labyrinth formed by the outer surface of the central part and the inner surface of the detachable parts of the housing.
What is the speed of filling of overmolding?
Firstly, the mold steps, at first the melt enters slowly to the level of the collector, where it closes the electrical contact, turns on the additional pressure of the pneumatic system, and quickly fills the mold cavity.
At the end of filling the mold cavity, the melt, closing the second contact of the electrical interlock, turns on a device that maintains the pressure in the crucible at the reached level until the overmolding is completely solidified.
How many types of molding machines?
In addition, when the overmolding completely solidifies, the so-call technological holding time switch activates, and the pressure in the crucible is automatically released. The mold is opened and the molded part is ejected. It makes it possible to obtain thin-walled molded parts in various forms.
Currently, more than 20 varieties of thermoplastic for injection molding are known. Each type can be for certain types of products. Plastic can be used in universal or specially equipped injection molding machines, equipment, and technological methods.
Traditional injection molding
The most common type of injection molding carries out on universal injection molding machines (IMCs) and is used to manufacture parts with a wall thickness of 1.5 to 5 mm. The share of parts obtained by traditional overmolding exceeds 90% of the total number of molded thermoplastic parts.
Besides, injection molding (compression molding, press molding) involves the injection of a melt into a mold that is not completely closed. The final molding with increasing pressure in the mold occurs at the final closing of the mold. Injection molding produces simple-shaped parts of increased thickness.
Is the overmolding process at high speed?
Moreover, it has high-speed thin-walled overmolding for products with a wall thickness of 0.6 to 1.2 mm. It has its own characteristics in terms of overmolding units equipped with a hydraulic accumulator. Special equipment with a developed ventilation system, and overmolding modes that are fundamentally different from traditional overmolding.
Overmolding has thick-walled parts with a thickness of 10–30 mm. It carries out according to a technology close to traditional overmolding. It distinguishes by 2–4 times longer holding time under pressure and cooling, and at the same time, the sprue diameter increases by 2–3 times.
How many producing stages of overmolding?
Furthermore, the overmolding process produces molded parts in two stages. In the first stage, the mold is partially filled with the melt during the rotation of the screw (similar to extrusion).
The final filling of the mold, holding under pressure occurs during the translational movement of the screw-piston forward without rotation. This method is used when the volume of the molded part exceeds the maximum injection volume of the injection molding machine.
How is Sandwich overmolding characterized?
Firstly, sandwich overmolding is by successive injection of two polymers through one sprue. The first polymer is creating a surface layer from a color primary polymer, and the second polymer, as if from the inside, inflates the surface layer. The inner layer can recycle or expandable polymer. The injection molding machine must equip with two injection units.
Two-component or two-color injection molding is characterized by the successive injection of different polymers using several mold cavities of different geometric shapes and volumes.
First, a plastic insert is a substrate, which moves with the mold half into another molding cavity of a larger volume. Where the insert fills with another polymer. The polymers must have good adhesion to each other. The machine equips with two injection units.
The molding machine uses high injections rates
In fact, foam molding of expandable thermoplastics carries out using high injection rates on hydraulic accumulator injection molding machines. The original thermoplastic contains a physical blowing agent (for example, isopentane) or a chemical blowing agent. There are super concentrates containing a blowing agent.
How does the molding machine work?
In addition, overmolding with gas begins with an incomplete injection of the melt. Then gas (usually nitrogen) supplies to the melt through the sprue or, directly, into the mold, bypassing the sprue. As well, gas under pressure of 50 – 120 kg/cm2 inflates the polymer shell, and presses the polymer from the inside to the inner surface of the cavity, eliminating sinks.
The structure of the overmolding has a pronounced gas cavity surrounded by a monolithic polymer. Gas injection is used for thick-walled products that do not require a monolithic polymer section.