General structure
How many types of injection moulding machines? Injection moulding machines generally consist of two parts: the injection unit, which prepares the plastic granules and injects them under pressure into the tool, as well as the closing unit, which picks up the tool and opens/closes it.

Three-zone screw
The three-zone screw is often used in thermoplastic processing. In the so-call feed zone, the plastic granules are drawn in and conveyed to the next zone, the compression zone, where the plastic is plasticized and compressed (degassed).
The melt is then homogenized in the metering zone and finally pushed through the non-return valve in front of the screw, which moves axially backward as a result of the increasing dynamic pressure in the barrel.
Non-return valve
How many types of injection moulding machines? The reverse flow lock prevents the volume of mass in front of the screw from flowing back into the screw flights when injecting and squeezing so that the screw acts as a piston. The non-return valve is located at the end of the screw and usually consists of three parts:
During dosing, the melt presses the locking ring against the tip of the screw. It creates a gap between the locking ring and the pressure ring (locking ring stroke) through which the melt can flow.
How many types of injection moulding machines? When the fuel is injected, the locking ring presses against the pressure ring and thus closes the screw threads. The distance between the locking ring and the barrel is called the worm clearance.
Moulding machine Locking unit
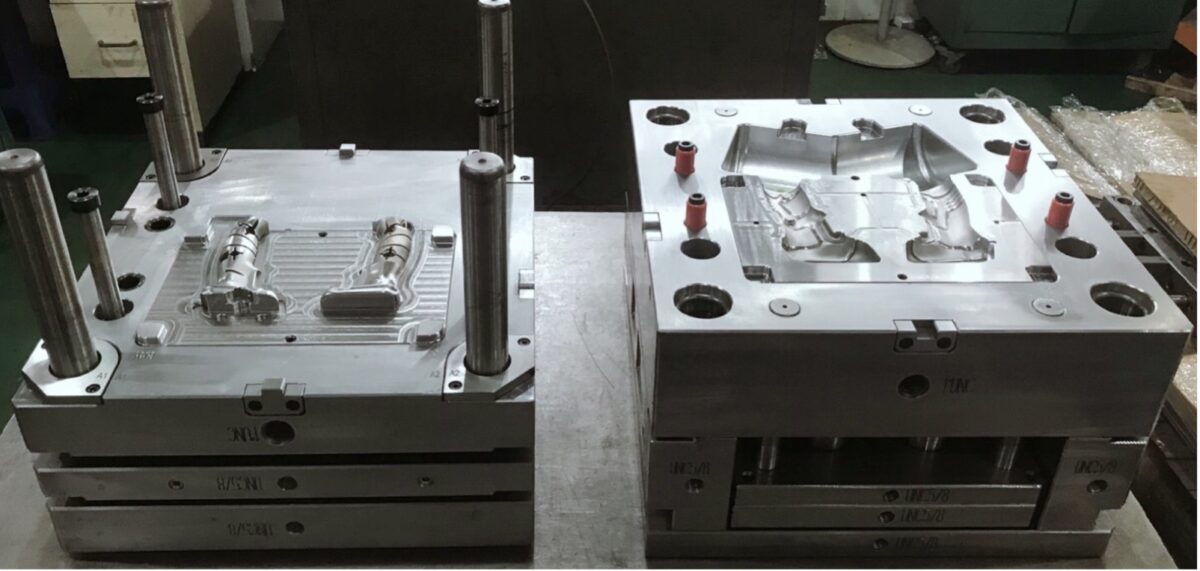
The clamping unit usually consists of three plates, which are arranged vertically on one axis on a machine frame. The fixed platen carries half of the mold (nozzle side) and is the plate closest to the injection unit. The fixed platen has a hole in the middle through which the nozzle can pass and dock onto the tool. The second platen is the moveable platen.
The second half of the mold (ejector side) is mounted on it. It is movable and is pushed mechanically or hydraulically in the direction of the fixed platen.
How many types of injection moulding machines?
Since the two tool halves are pushed together, this is referred to as closing. Finally, the third plate is the front plate. It has a supporting function because the toggle lever or the hydraulic cylinder is for closing the clamping plates. It is located between the faceplate and the movable clamping plate.
The faceplate is therefore necessary to build up the force. The ejector is also located on the movable clamping plate; these are hydraulic cylinders that actuate small metal pins in the mold when the mold is open, which then presses the molded part out of the mold.
There are also connections for core pulls here. This can be used to actuate slides in the tool; these are movable areas in the mold in order to be able to produce undercuts.
The forces acting on the clamping unit are defined (according to DIN 24450) as follows:
- Closing force
- locking force
- Buoyancy
- (Maximum) Mold opening force
- Ejector force
Moulding machine Process
How many types of injection moulding machines? The process depends on many things. However, there is always a basic scheme in which further steps can be integrated as required.
At the beginning of the cycle, the mass volume is metered, and the mold is open. First, the mold is closed and the injection unit is moved up to the mold. Then the moulding plastic is injected. After a certain waiting time for the moulding compound to cool down or react, metering is carried out, and the injection unit is lifted off again.

Types of injection moulding machines
How many types of injection moulding machine? Another difference is the way in which the force in the clamping unit (clamping force) is built up. A distinction is made between hydraulic machines, in which the mold is built up and held by large hydraulic cylinders, and toggle machines, in which a large, double-acting toggle presses the tool together.
The toggle lever itself is in turning and also moved either by a hydraulic cylinder. In the case of an electric machine, by an electric motor, the mechanics of the lever require significantly less force to hold the mold together than with exclusively hydraulic systems.
How many types of injection moulding machines?
There are also some special forms, such as the two-platen clamping unit. Here the tool is not pressed together from behind but pulled together hydraulically. Due to the special structure, special, large tools can be used.
There are also electric series in which the closing force is generated by electric motors. However, this is only possible on machines with very low clamping forces, since electric motors cannot provide a good compromise between power and speed.
Injection moulding machine Special types
How many types of injection moulding machines? Multi-component injection moulding machines offer the possibility of producing the frequently required complex molded parts from different colors or types of plastic in a single process. In addition to the classic multi-color and hard-soft combinations, various special processes can also be implemented with multi-component machines.
Another type is the electric injection moulding machines, in which all axes are driven electrically. The clasps are built as toggle levers.
Size information about moulding machine
How many types of injection moulding machines? The information that can be used to evaluate and assess the size of an injection moulding machine is specified in the standard.
Since an injection moulding machine consists of two parts, the injection unit, and the clamping unit, clear parameters are given there. After that, an injection moulding machine is characterized by:
The closing force with which the tool is compressed, specified in kN (kilo- Newton)
The calculated stroke volume of the injection unit in cm³ is based on an injection pressure of 1000 bar. In other words, the amount of moulding compound is that the injection unit can inject into the clamping unit at a pressure of 1000 bar.