CONTENTS
- What is injection molding?
- Construction of an injection molding machine
- What injection molding processes are there?
- Thermoplastic injection molding
- Thermoset injection molding
- Elastomer injection molding
- What advantages does injection molding have?
1. WHAT IS INJECTION MOLDING?
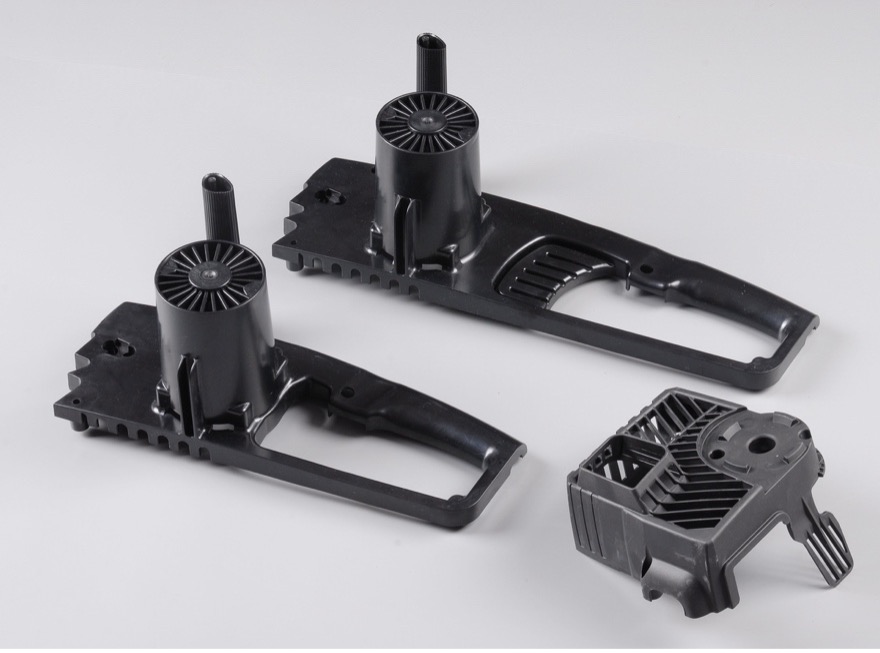
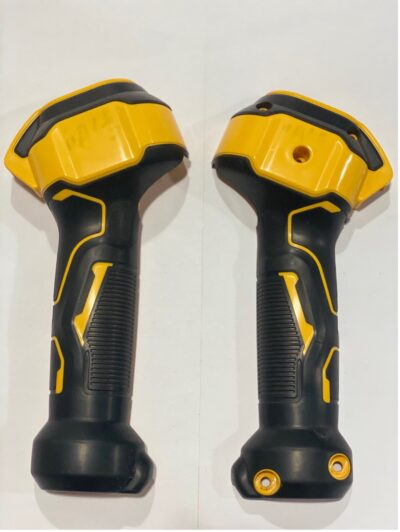
How is injection molding done? Firstly, Injection molding is mainly used in plastics processing and uses to manufacture small parts and prototypes almost exclusively from plastics. Injection molding is the most common manufacturing method for prototyping and low-volume production of consumer parts.
In injection molding, a mechanism occurs where thermoplastic or thermoset polymers are injected into a cavity and then solidified as a finished part.
The solidified material is then ejected from the mold. With this injection molding process, molded parts can be produced economically in large quantities. An injection molding machine also produces these objects with high accuracy and in a short time.
Construction of an injection molding machine
How is injection molding done? Nowadays parts from a few tenths of a gram up to the two-digit kilogram range can be manufactured. In addition, the surface of the component can be selected almost freely in injection molding. The injection molding process uses to produce smooth surfaces, grains, patterns, and engravings.
After the plastic mass cools down in the injection molding tool, the tool can be opened to remove the plastic component.
When it cools down, the material returns to a solid-state.
What injection molding processes are there?
How is injection molding done? The injection molding process makes economic sense for larger quantities. The costs for tool-making are a large part of the necessary investments. As a result, even with simple tools, the investment only pays off after a few thousand parts have been manufactured. The injection molding tool can use to produce up to a few million parts.
This makes injection molding the most common method for mass production of plastic objects. Injection molding is preceded by tool-making to produce injection molds for various injection molding processes.
The plastic injection molded parts are classified into categories as follows
How is injection molding done? Parts are very precise parts with the highest requirements, technical plastic parts with high requirements, or geometric simple moldings made of plastic with low requirements.
All categories have, among other things, the following essential quality characteristics: molded part dimensions and weight, surface structure, strength, and signs of warping.
Do you need further information on the subject of injection molding? Then simply contact us by the contact form on our homepage, telephone, or e-mail!
2. STRUCTURE OF AN INJECTION MOLDING MACHINE
How is injection molding done? The worm-piston injection molding machine basically consists of two parts. The injection unit or plasticizing unit plasticizes the plastic, prepares it, and doses it, and the closing unit closes, holds, and opens the mold.
The injection unit consists mainly of the plasticizing cylinder, a horizontal cylinder, and a screw located inside. At one end of the plasticizing cylinder, there is a hopper for filling with the raw material; at the other, there is a nozzle that can be either closable or non-closable. Furthermore, it locates between the plasticizing cylinder and the clamping unit and serves as a transition.
3. WHAT INJECTION MOLDING PROCESSES ARE THERE?
How is injection molding done? The material that is processed during injection molding can be divided into thermoplastics, duroplastics, and elastomers. Eventually, all three types of plastic can use for injection molding. However, the process most widely uses for plastic processing is thermoplastic injection molding, as it is the most economically important.
The injection molding process for duroplastics and elastomers works in principle like the process for thermoplastics and mainly differs in terms of parameters such as temperatures.
3.1. THERMOPLASTIC INJECTION MOLDING
How is injection molding done? The thermoplastic material trickles into the rotating screw as granules. The granules heat and melt by the heat in the tool. The melted granulate accumulates in front of the screw tip because the nozzle is still closed.
In the injection phase, the plasticizing unit moves to the closing unit, pressed with the nozzle and the screw pressurizes. Moreover, the molten plastic is pressed under high pressure through the open nozzle, which creates a cavity. The non-return valve prevents the melt from flowing back.
After the end of the pressing, the nozzle can close and the plasticizing and dosing process for the next molded part can begin in the injection unit. The material in the mold continues to cool down during the remaining cooling time until the core, the liquid core of the workpiece, has solidified and sufficient rigidity has been reached for demoulding.
3.2. THERMOSET INJECTION MOLDING
How is injection molding done? Compared to thermoplastic injection molding, thermoset injection molding is mostly cured by exposure to heat. After Duroplast has hardened, it can no longer melt again. However, thermosets can recycle.
The mass that has not yet hardened must therefore be injected into the mold at a lower temperature and then be hardened there at a higher temperature. With thermoset injection molding, parts with very large wall thicknesses of up to 50 mm can form.
Thermosets are typically used for vehicle headlights, among other things. Although the material price of duroplastics is generally cheaper, they usually lose out compared to thermoplastics in the comparison of economic efficiency.
3.3. ELASTOMER INJECTION MOLDING
How is injection molding done? Likes duroplastics, elastomers vulcanize under the influence of heat. The tool must therefore also be hotter than the molding compound during the injection process. The thermoplastic elastomers are an exception.
Elastomers can be drawn in by a special screw conveyor in the form of free-flowing powders or in the form of strips. The cylinder is usually heated to approx. 80 °C by means of water temperature control in order to avoid overheating. Since molten elastomers are very fluid, the effort involved in designing the tool is higher than with thermoplastic tools.
Apart from the special features, the injection molding process is basically similar to thermoplastic injection molding.